Topic 2: Understand Web Components
Topic 2.1 Hardware and Software Components
Hardware
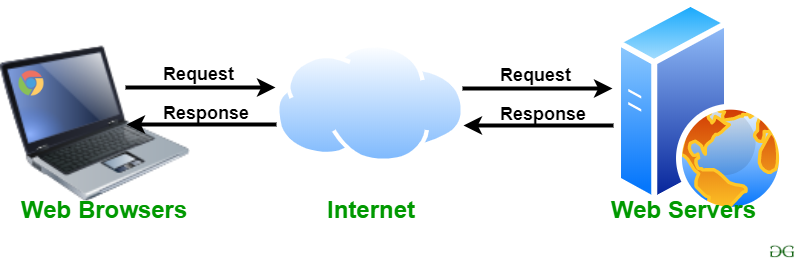
Webserver: A web server is software that allows users to view webpages, through web browsers. When a website is typed into the URL bar, a browser sends a request to the web server, which then renders the page in your browser.
Client: Clients can be machines (laptop, computer, phone), or programmes (web browsers, word processors etc. A client is used to make requests through the web.
Routers: Routers are devices which forward data packets, between different computer networks. They join networks together e.g. connecting your home network to the internet. Routers can be wired to devices, or can be wireless.
Mail Servers: Mail Servers are what emails pass through when they are sent, either outgoing or incoming. Once you send an email, your email client connects to a server and provides it with the information (content, recipient, attachments) and the server locates the recipient's server, and transfers the information.
Software
Content Management Systems: A Content Management System (CMS) is an application which has the capability to create, store, edit, manage and publish large amounts of content - with the user not requiring programming skills to use.
Browsers: A browser is a program that allows you to visit websites. Every webpage runs through browsers, and they are free to download.
Web Authoring Software: Web authoring software allows the creation of web pages, in a way that doesn’t require the user to directly write the code e.g. WordPress, Umbraco.
Databases: Databases are used to manage and organise data, such as usernames, email addresses and encrypted passwords.
Topic 2.2 Protocols
HTML: Hypertext Transfer Protocol. Hypertext is when there are links in text, HTTP is the protocol on how to transfer hypertext from web servers to web browsers. So how the links become visible within text on the browser, and available for users to use. Based on the client/server model, for example when the client (computer, phone, tablet) requests the server (website, application), the server responds to the request using HTTP rules. Ensures both the client and the server understand each other.
HTTPS: If using wireless networks, other clients on the network can potentially tap your data. The same can be done for wired networks, if the wire is directly wire tapped. To secure this connection, HTTPS can be used. HTTPS is a way to encrypt information sent across the internet, this can extend as far as encrypting domain names but also passwords, financial information etc. Prevents users from having information stolen and secures websites.
FTP: FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol, allows data to be transferred between two computers over an internet connection.
SMTP: SMTP is Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, the protocol that allows you to send email to a mail server.
TCP: TCP is Transmission Control Protocol makes data transfer reliable, ensuring data arrives at its destination.
Topic 2.3 Web Technologies
Domains and Webhosting Services: A domain is the web address for your website. These can be purchased, and customised as long as the domain name isn’t already taken. Having a domain name makes it so that users can find your website.
DNS: Stands for Domain Name System. The DNS looks up the correct IP address that matches a domain name, and sends a user to that particular website.
IP Address: An IP address provides information about where your device is geographically. Consists of a unique set of numbers specific to a device.
Security: To avoid being tracked, there are ways to hide an IP address including using VPN’s. The server that you’re connecting to will not be able to see your geographical location. There are ‘incognito’ modes on most browsers, which will reduce the number of cookies, but this is not totally effective.
Topic 2.4 Search Engines
Crawling and Indexing: Google uses ‘spiders’ to crawl the web, to discover content to place it accordingly into search results. As the content is crawled, a copy is stored on Google’s servers, which is Google’s index. When a user searches, Google checks the index for everything relevant to the search phrase.
Relevance and Popularity: Google uses an algorithm to check everything relevant in the index, and rank them based on this relevancy. There are many ranking factors e.g. content, linked content, website quality.
Meta Information: Meta information is the information displayed about a page when it shows up on a search engine, so the title, description and keywords tags. Having good meta information encourages users to open the page, and will encourage the listing to go higher in Google’s search ranking.
Artifical Influencing: Artificial intelligence are future predictions based on past data, when done technologically the predictions can be very accurate and used to inform future marketing techniques.